区间dp训练
石子合并(弱化版)
题目描述
设有 \(N(N \le 300)\) 堆石子排成一排,其编号为 \(1,2,3,\cdots,N\)。每堆石子有一定的质量 \(m_i\ (m_i \le 1000)\)。现在要将这 \(N\) 堆石子合并成为一堆。每次只能合并相邻的两堆,合并的代价为这两堆石子的质量之和,合并后与这两堆石子相邻的石子将和新堆相邻。合并时由于选择的顺序不同,合并的总代价也不相同。试找出一种合理的方法,使总的代价最小,并输出最小代价。
输入格式
第一行,一个整数 \(N\)。
第二行,\(N\) 个整数 \(m_i\)。
输出格式
输出文件仅一个整数,也就是最小代价。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
1 | 4 |
样例输出 #1
1 | 22 |
前缀和+区间dp
1 |
|
[IOI1998] Polygon
题面翻译
题目可能有些许修改,但大意一致
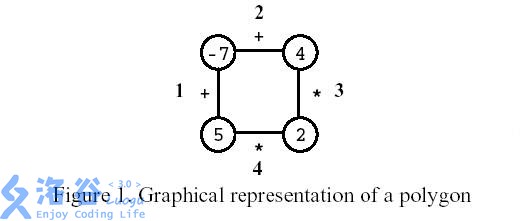
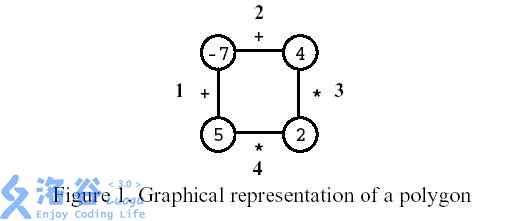
多边形是一个玩家在一个有n个顶点的多边形上的游戏,如图所示,其中n=4。每个顶点用整数标记,每个边用符号+(加)或符号*(乘积)标记。
第一步,删除其中一条边。随后每一步:
选择一条边连接的两个顶点V1和V2,用边上的运算符计算V1和V2得到的结果来替换这两个顶点。
游戏结束时,只有一个顶点,没有多余的边。
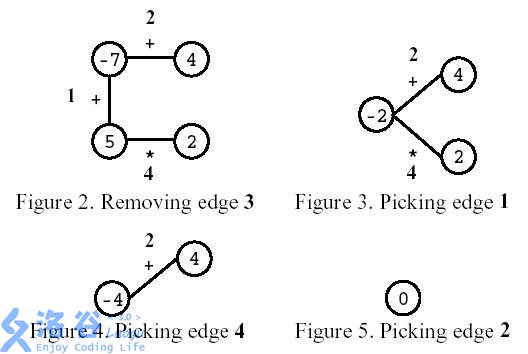
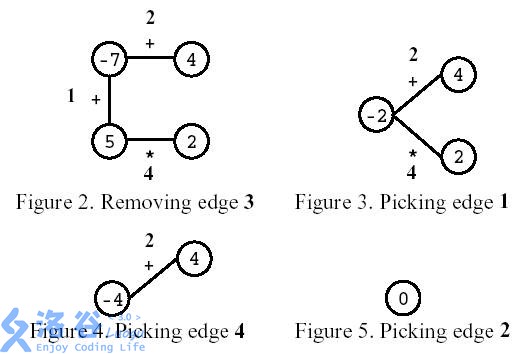
如图所示,玩家先移除编号为3的边。之后,玩家选择计算编号为1的边,然后计算编号为4的边,最后,计算编号为2的边。结果是0。
(翻译者友情提示:这里每条边的运算符旁边的数字为边的编号,不拿来计算)
编写一个程序,给定一个多边形,计算最高可能的分数。
输入格式
输入描述一个有n个顶点的多边形,它包含两行。第一行是数字n,为总边数。
第二行描述这个多边形,一共有2n个读入,每两个读入中第一个是字符,第二个是数字。
第一个字符为第一条边的计算符号(t代表相加,x代表相乘),第二个代表顶点上的数字。首尾相连。
3 < = n < = 50
对于任何一系列的操作,顶点数字都在[-32768,32767]的范围内。
输出格式
第一行,输出最高的分数。在第二行,它必须写出所有可能的被清除后的边仍能得到最高得分的列表,必须严格递增。
感谢@2016c01 提供的翻译
题目描述
Polygon is a game for one player that starts on a polygon with \(N\) vertices, like the one in Figure 1,
where \(N=4\). Each vertex is labelled
with an integer and each edge is labelled with either the symbol
+ (addition) or the symbol * (product). The
edges are numbered from \(1\) to \(N\).
On the first move, one of the edges is removed. Subsequent moves involve the following steps:
- pick an edge \(E\) and the two vertices \(V_1\) and \(V_2\) that are linked by \(E\); and
- replace them by a new vertex, labelled with the result of performing the operation indicated in \(E\) on the labels of \(V_1\) and \(V_2\).
The game ends when there are no more edges, and its score is the label of the single vertex remaining.
Consider the polygon of Figure 1. The player started by removing edge 3. After that, the player picked edge 1, then edge 4, and, finally, edge 2. The score is 0.
Write a program that, given a polygon, computes the highest possible score and lists all the edges that, if removed on the first move, can lead to a game with that score.
输入格式
Your program is to read from standard input. The input describes a polygon with N vertices. It contains two lines. On the first line is the number N. The second line contains the labels of edges 1, ..., N, interleaved with the vertices' labels (first that of the vertex between edges 1 and 2, then that of the vertex between edges 2 and 3, and so on, until that of the vertex between edges N and 1), all separated by one space. An edge label is either the letter t (representing +) or the letter x (representing *).
3 <= N <= 50
For any sequence of moves, vertex labels are in the range [-32768,32767].
输出格式
Your program is to write to standard output. On the first line your program must write the highest score one can get for the input polygon. On the second line it must write the list of all edges that, if removed on the first move, can lead to a game with that score. Edges must be written in increasing order, separated by one space.
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
1 | 4 |
样例输出 #1
1 | 33 |
第一步:断环为链
第二步:考虑最大值
加法就正常区间dp
乘法要考虑最小值得存储
1 |
|
金字塔(区间DP+dfs序)
(s[k]==s[l])可分割为两颗子树得条件
必须是同一个根节点
1 |
|